
Nominal vs. Real Interest Rate - Effects of Inflation
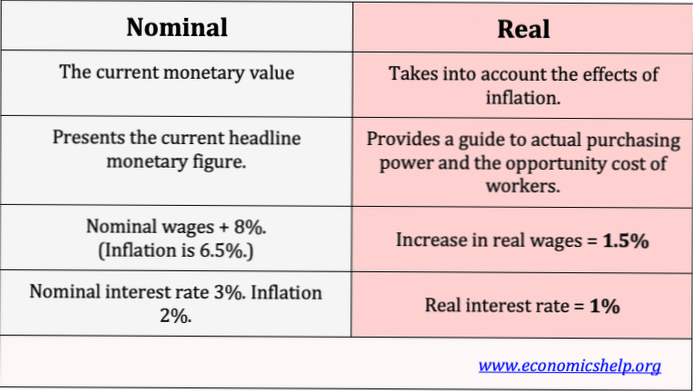
A real interest rate is the interest rate that takes inflation into account. This means it adjusts for inflation and gives the real rate of a bond or loan. ... The calculation used to find the real interest rate is the nominal interest rate minus the actual or expected inflation rate.
- Does inflation affect nominal interest rates?
- How inflation affects real interest rates?
- How are inflation rates real interest rates and nominal interest rates related to each other?
- What happens when nominal interest rates increase?
- What is nominal and effective interest rate?
- Why is inflation 2%?
- What affects the real interest rate?
- Who benefits from inflation?
- Why is inflation bad for savings?
- Do real and nominal interest rates always move together?
- What is the relationship between nominal and real interest rate?
- Is nominal interest rate always higher than real interest rate?
Does inflation affect nominal interest rates?
When expected inflation changes, the nominal interest rate will increase. However, inflation will not affect the real interest rate.
How inflation affects real interest rates?
According to the quantity theory of money, a growing money supply increases inflation. Thus, low interest rates tend to result in more inflation. High interest rates tend to lower inflation.
How are inflation rates real interest rates and nominal interest rates related to each other?
real interest rate ≈ nominal interest rate − inflation rate. To find the real interest rate, we take the nominal interest rate and subtract the inflation rate. For example, if a loan has a 12 percent interest rate and the inflation rate is 8 percent, then the real return on that loan is 4 percent.
What happens when nominal interest rates increase?
As the interest rate increases, this opportunity cost increases, and the quantity of money demanded decreases as a result. ... When nominal GDP decreases, the demand for money shifts to the left, and, when nominal GDP increases, the demand for money shifts to the right.
What is nominal and effective interest rate?
Effective interest rate is the one which caters the compounding periods during a payment plan. ... The nominal interest rate is the periodic interest rate times the number of periods per year. For example, a nominal annual interest rate of 12% based on monthly compounding means a 1% interest rate per month (compounded).
Why is inflation 2%?
To keep inflation low and stable, the Government sets us an inflation target of 2%. This helps everyone plan for the future. If inflation is too high or it moves around a lot, it's hard for businesses to set the right prices and for people to plan their spending.
What affects the real interest rate?
Interest rate levels are a factor of the supply and demand of credit: an increase in the demand for money or credit will raise interest rates, while a decrease in the demand for credit will decrease them.
Who benefits from inflation?
Inflation allows borrowers to pay lenders back with money that is worth less than it was when it was originally borrowed, which benefits borrowers. When inflation causes higher prices, the demand for credit increases, which benefits lenders.
Why is inflation bad for savings?
Inflation not only affects the cost of living – things such as transport, electricity and food – but it can also impact interest rates on savings accounts, the performance of companies and in-turn, share prices. As measures of inflation rise, this reflects a reduction in the purchasing power of your money.
Do real and nominal interest rates always move together?
Real interest rates and nominal interest rates can be either positive or negative. ... Nominal and real interest rates do not always move together.
What is the relationship between nominal and real interest rate?
A real interest rate is an interest rate that has been adjusted to remove the effects of inflation to reflect the real cost of funds to the borrower and the real yield to the lender or to an investor. A nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate before taking inflation into account.
Is nominal interest rate always higher than real interest rate?
With positive inflation, the nominal interest rate is higher than the real interest rate. Effectively, the real interest rate is the nominal interest adjusted for the rate of inflation. ... Example: If the rate of inflation is at 3%, and the real interest rate is 2%, then the nominal interest rate would be 5%.



Yet No Comments