
at what age do you not have to pay taxes on an ira
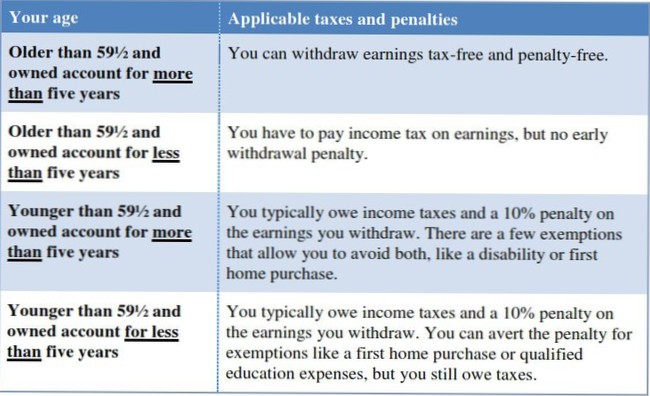
When You Owe Income Tax on a Withdrawal Once you reach age 59½, you can withdraw money without a 10% penalty from any type of IRA. If it is a Roth IRA and you've had a Roth for five years or more, you won't owe any income tax on the withdrawal.
- How can I avoid paying taxes on my IRA?
- Can you let money stay in an IRA until age 75?
- How much tax do you pay when you withdraw from your IRA?
- Do you have to pay income tax on your IRA?
- At what age is 401k withdrawal tax free?
- Can I withdraw all my money from my IRA at once?
- Do pensions count as earned income?
- How long does it take to cash out an IRA?
- Can you contribute to your IRA if you are on Social Security?
- Which states do not tax IRA withdrawals?
- Can I withdraw money from my IRA to pay off mortgage?
- Do IRA withdrawals count as income?
How can I avoid paying taxes on my IRA?
Here's how to minimize 401(k) and IRA withdrawal taxes in retirement:
- Avoid the early withdrawal penalty.
- Roll over your 401(k) without tax withholding.
- Remember required minimum distributions.
- Avoid two distributions in the same year.
- Start withdrawals before you have to.
- Donate your IRA distribution to charity.
Can you let money stay in an IRA until age 75?
No matter how old you are, you can continue to contribute to your Roth IRA as long as you're earning income—whether you receive a salary as a staff employee or 1099 income for contract or freelance work. On the flip side, you never have to take distributions from the account either.
How much tax do you pay when you withdraw from your IRA?
If you withdraw money from a traditional IRA before you turn 59 ½, you must pay a 10% tax penalty (with a few exceptions), in addition to regular income taxes. Plus, the IRA withdrawal would be taxed as regular income, and could possibly propel you into a higher tax bracket, costing you even more.
Do you have to pay income tax on your IRA?
Contributions to traditional IRAs are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals are subject to income tax. ... Because contributions to Roth IRAs are made with after-tax money, they can be withdrawn at any time, for any reason.
At what age is 401k withdrawal tax free?
The IRS allows penalty-free withdrawals from retirement accounts after age 59 ½ and requires withdrawals after age 72 (these are called Required Minimum Distributions, or RMDs). There are some exceptions to these rules for 401ks and other qualified plans.
Can I withdraw all my money from my IRA at once?
Age 59½ and over: No withdrawal restrictions
Once you reach age 59½, you can withdraw funds from your Traditional IRA without restrictions or penalties.
Do pensions count as earned income?
For the year you are filing, earned income includes all income from employment, but only if it is includable in gross income. ... Earned income does not include amounts such as pensions and annuities, welfare benefits, unemployment compensation, worker's compensation benefits, or social security benefits.
How long does it take to cash out an IRA?
Delivery times and fees
| Method | Delivery times | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) | 1–3 business days | None |
| Bank wire | Immediately* | None† |
| A paper check | 5–6 business days | None |
| Transfer between Fidelity accounts | Immediately | None |
Can you contribute to your IRA if you are on Social Security?
Income. You can open and make contributions to a Roth IRA in any year that you have earned income, and you can contribute 100 percent of your earned income, up to the maximum allowed by law, each year. ... You can make contributions even if you are on Social Security, but you can't contribute more than your earned income.
Which states do not tax IRA withdrawals?
Nine of those states that don't tax retirement plan income simply have no state income taxes at all: Alaska, Florida, Nevada, New Hampshire, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Washington and Wyoming. The remaining three — Illinois, Mississippi and Pennsylvania — don't tax distributions from 401(k) plans, IRAs or pensions.
Can I withdraw money from my IRA to pay off mortgage?
Your monthly withdrawal from your IRA will be treated as taxable income, but you'll be receiving a tax deduction for the majority of your mortgage payment, essentially eliminating the income tax consequences.
Do IRA withdrawals count as income?
Withdrawals from IRAs are taxable income and Social Security benefits can be taxable. ... If you never made any nondeductible contributions to any of your IRA accounts, all of the IRA withdrawal is counted as taxable income.



Yet No Comments